In modern architecture and infrastructure, every detail matters — from design precision to the materials that hold structures together. Yet one of the most important but often overlooked factors behind building durability is coating construction.
Coatings act as protective shields, enhancing the longevity, performance, and appearance of structures. From skyscrapers and industrial plants to bridges and residential homes, the right coating can make the difference between decades of resilience and early deterioration.
In this article, we’ll explore what coating construction is, why it’s essential, its various types, how to choose the right one, and best practices for application — all while highlighting how it ensures long-lasting quality in modern buildings.
What Is Coating Construction?
Coating construction refers to the process of applying specialized surface treatments to protect, seal, or beautify different building materials. These coatings are often liquid or powder-based compounds applied on concrete, steel, wood, or masonry during or after construction.

Their main purpose is to protect structures from external damage such as corrosion, UV rays, moisture, heat, or chemicals. Beyond protection, coatings also add aesthetic appeal — providing color, texture, and shine that enhances the building’s overall appearance.
In essence, coating construction is a science of combining chemistry and engineering to achieve lasting performance.
- Also read: What Are Construction Coatings And Their Uses?
Why Coating Construction Matters
Construction coatings are not merely decorative — they play a structural and economic role in extending the lifespan of a building. Here are several reasons why coating construction is vital for any project:
1. Protection Against Environmental Damage
Buildings are constantly exposed to harsh weather, UV rays, rain, pollution, and humidity. Without a proper coating system, these elements can deteriorate materials quickly. Coatings create a durable barrier that prevents damage, especially on concrete and steel.
2. Corrosion Resistance
Steel structures, bridges, and pipelines are prone to corrosion. Protective coatings such as epoxy or zinc-rich primers act as anti-corrosive shields, preventing oxidation and rust formation.
3. Waterproofing
Water infiltration can cause severe problems like cracks, mold, and weakening of foundations. Coating construction provides an impermeable layer that blocks moisture penetration and ensures structural safety.
4. Enhanced Aesthetics
Apart from protection, coatings improve the appearance of surfaces. They offer a clean finish, glossy texture, or even a matte look, helping architects achieve visual goals.
5. Extended Lifespan and Lower Maintenance
By minimizing physical wear and chemical degradation, coatings significantly increase the life of a structure. This reduces the need for frequent repairs, leading to long-term savings.
6. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Reflective and insulating coatings help in maintaining interior temperatures by reducing heat absorption. This not only cuts down on cooling costs but also promotes environmental sustainability.
Types of Coatings Used in Construction
Different coatings serve different purposes based on environmental conditions, material type, and project requirements. Here are the main categories of coatings used in modern construction:

1. Architectural Coatings
These are primarily decorative coatings used for interior and exterior walls. They enhance aesthetics while providing protection against environmental wear. Examples include:
- Latex paints
- Acrylic coatings
- Masonry finishes
Architectural coatings are often breathable, allowing moisture vapor to escape without damaging the wall.
2. Protective or Industrial Coatings
Protective coatings are applied on steel structures, pipelines, bridges, and machinery to prevent corrosion. Common types include:
- Epoxy coatings
- Polyurethane coatings
- Zinc-rich primers
They are highly durable, chemical-resistant, and suitable for high-exposure environments.
3. Waterproofing Coatings
These coatings protect surfaces like basements, roofs, and balconies from water damage. Examples include:
- Bituminous coatings
- Elastomeric membranes
- Cementitious waterproof coatings
Waterproof coatings are essential for maintaining the integrity of structural components exposed to moisture.
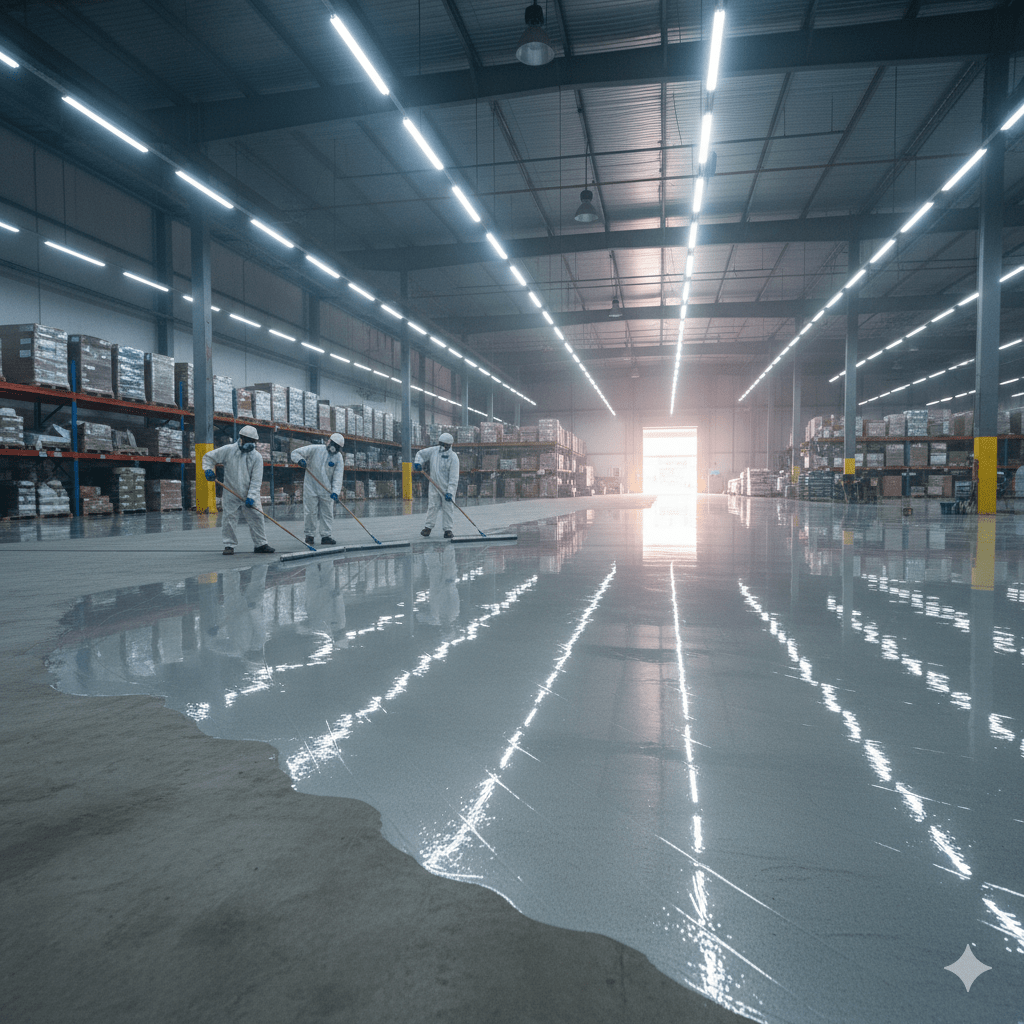
4. Floor Coatings
Industrial and commercial spaces use epoxy or polyurethane floor coatings for abrasion resistance, chemical protection, and a clean finish.
They are ideal for:

- Warehouses
- Hospitals
- Parking areas
- Garages
5. Thermal and Reflective Coatings
Used primarily on roofs, these coatings reflect sunlight, lower heat absorption, and reduce cooling loads. They are eco-friendly and contribute to sustainable building design.
6. Powder Coatings
Powder coatings are applied as dry powders and cured under heat. They form a hard, protective layer that is extremely durable and resistant to scratches and fading.
Common uses include metal railings, doors, and decorative panels.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Coatings
Selecting the right coating for a construction project is critical. The wrong choice can lead to peeling, cracking, or corrosion within months. Here are the main factors to consider:
1. Type of Substrate
Each material — steel, concrete, wood, or masonry — requires specific coating chemistry for proper adhesion and performance.
2. Exposure Conditions
Consider the environment: Is it humid, coastal, industrial, or high-UV? Coastal and industrial areas, for example, demand high-performance anti-corrosive coatings.
3. Application Method
Some coatings are spray-applied, while others require rollers or brushes. The choice depends on the project scale, accessibility, and desired finish.
4. Durability Requirements
High-traffic or heavy-duty environments require stronger coatings that resist abrasion and chemical exposure.
5. Aesthetic Goals
The finish, gloss level, and color retention are important for visible surfaces such as façades and interiors.
6. Compliance with Standards
Always choose coatings that meet international or local standards (ASTM, ISO) to ensure long-term reliability.
Best Practices for Applying Construction Coatings
Even the best coating fails if not applied correctly. Follow these professional steps for maximum protection and longevity:
1. Surface Preparation
Surface preparation accounts for nearly 70% of coating success. Clean the substrate thoroughly — remove rust, dust, oil, or old paint. Use sandblasting or acid cleaning if necessary.
2. Priming
Use a compatible primer before applying the main coating. Primers promote adhesion and block surface contaminants.
3. Correct Application
Apply coatings under recommended temperature and humidity conditions. Use proper tools like airless spray guns for even coverage.
4. Layering
For durability, apply multiple thin layers instead of one thick coat. Allow proper curing between coats.
5. Quality Testing
After application, measure film thickness, adhesion strength, and surface uniformity using appropriate testing devices.
6. Maintenance
Inspect coated surfaces regularly for peeling, cracking, or discoloration. Minor touch-ups can prevent major restoration later.
Common Challenges in Coating Construction
Even with modern materials, coating construction faces a few common challenges:
- Moisture contamination during application
- Improper mixing of multi-component systems
- Poor surface preparation leading to delamination
- Temperature fluctuations affecting curing
- Incompatible layers between primer and topcoat
To avoid these, ensure all coatings are tested for compatibility and applied by trained professionals.
Future Trends in Coating Construction
The coating construction industry is evolving rapidly with the introduction of new materials and green technologies. Emerging trends include:
- Nanocoatings – offering superior scratch resistance and self-cleaning properties.
- Bio-based coatings – made from renewable materials, reducing VOC emissions.
- Smart coatings – capable of responding to temperature or humidity changes.
- 3D surface coatings – adding texture and depth to architectural surfaces.
These innovations promise higher efficiency, sustainability, and performance — aligning with modern building standards.
Conclusion
Coating construction is much more than an aesthetic choice — it’s a cornerstone of structural durability and protection. Whether shielding against corrosion, waterproofing, or improving thermal performance, coatings ensure buildings remain strong, safe, and visually appealing for decades.
By selecting the right type, preparing the surface properly, and following professional application standards, construction coatings can extend a building’s lifespan, minimize maintenance costs, and enhance its overall value.
In short, investing in quality coating construction means investing in lasting quality, sustainability, and long-term performance — the ultimate goals of every modern project.
- Also read: Andrew Tate Cars : A Symbol of Success and Power